What Do Milk Fat Percentages Mean?
Whether you want a glass of milk to go with homemade cookies or hot chocolate to warm up after playing in the snow, dairy products are a big part of food traditions. But, there are lots of options for milk in the supermarket aisle: skim, 1 percent, 2 percent, whole milk, plus flavored milks. How do you know what’s best for your family?
First, you can feel good knowing that all cow’s milk, regardless of type, contains the same nine essential nutrients, including calcium, vitamin D, potassium, protein, vitamin B-12 and vitamin A. Plus, all dairy products naturally contain milk protein, which helps build strong muscles for our active lifestyles. Learn more about nutrients and protein in milk at Midwest Dairy.
Milk Fat Percentages
The main difference between the different types of milk is how much fat they contain. But, what do milk fat percentages actually mean?
The percentage listed on your milk container is the amount of fat in the milk by weight.
- Whole milk is about 3.5 percent fat, and it’s the closest to the way it comes out of the cow.
- Reduced-fat is 2 percent fat.
- Low-fat is 1 percent fat.
- And fat-free, or skim, milk is, well, 0 percent fat
Choosing the right milk for you and your family is a matter of health considerations and personal taste.
So, how exactly does the fat content get adjusted? Some people think milk gets watered down, but that’s not the case! Before milk is bottled, all of the fat is removed. Then, it’s added back into the milk in the various percentages.
As the amount of fat varies, so do the total calories. For example, in an 8-ounce serving of milk:
- Skim has 80 calories
- Reduced fat has 120 calories
- Whole has 150 calories
All have the same 8g of protein, 30 percent of the daily calcium requirement and seven other essential nutrients.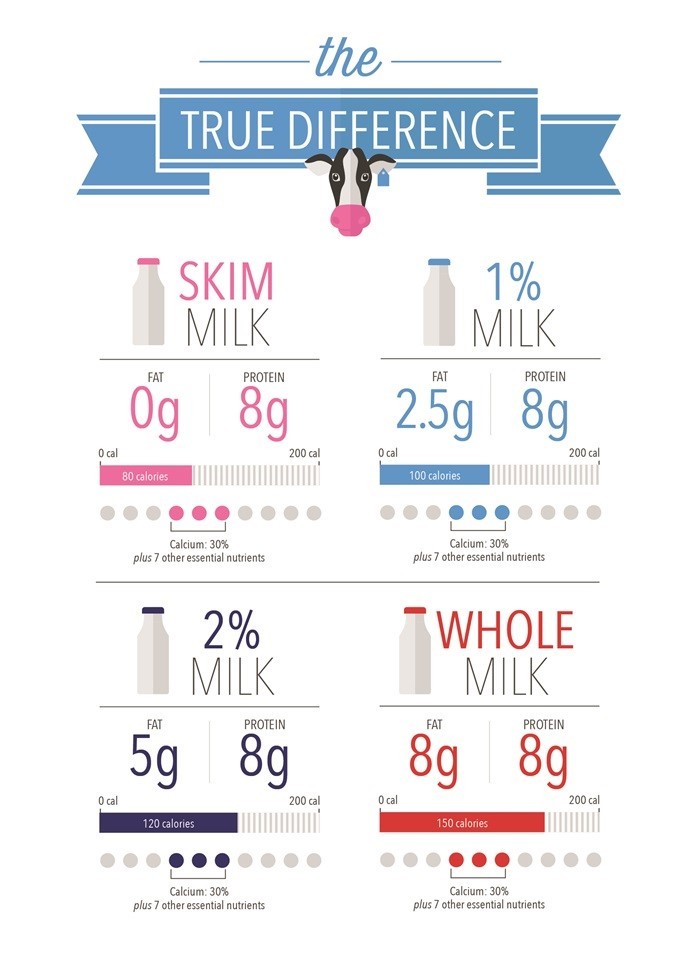
Flavored Milks
And what about chocolate, strawberry and other flavored milks? The addition of flavoring and sugar doesn’t take away any of the milk’s nutrients. Flavored milks have added sugars, but those account for less than 50 calories per serving. And, almost half of the sugar is naturally-occurring lactose which is found in all milk.
Drink for Your Health
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans categorize fat-free and low-fat dairy as nutrient dense foods. However, there is room for whole milk in a healthy diet, too. Some studies conducted over the past few years have shown that consumption of dairy products from whole milk or reduced fat milk is likely not associated with cardiovascular disease risk as once thought, and in some cases, saturated fat from dairy foods has actually been associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
Research is continuing in this arena, so stay tuned for more study results. In the meantime, talk to your health professional or registered dietitian to determine the right balance of higher and lower-calorie options for your individual health needs.




